In the mid-1950s, at the outset of his career and following the lead of his mentor Zoltán Glass, Adrian Flowers joined Artists Partners. An enterprise bringing together illustrators, graphic artists and photographers, Artists Partners was founded in 1950 by John Barker and G. Donovan Candler. Barker was a talented graphic artist who designed textiles for the Festival of Britain, while Candler had worked as an agent with an advertising company.

Other founding members included Betty Luton White, Reginald Mount (1906-1979) and Aubrey Rix, the latter designing many quintessential illustrations for Women’s Own. AP grew rapidly into a networking organisation for both artists and clients in London. Every Friday, a drinks party was held, initially at the AP headquarters at Lower John Street in Soho, and later at their more palatial offices in Dover Street, Mayfair. At these gatherings, creative talents and potential clients could get together to discuss projects and ideas. There was plenty of space at Dover Street, and several artists rented studio space there, including Adrian Flowers. He was commissioned by artists to take photographs as source material for illustrations, and also took on advertising work sent his way by Zoltán Glass.


Within three years, the number of participating artists at AP had reached fifty, among them Tom Eckersley, André François, Hans Unger and Heinz Kurth. Fashion artists such as Alistair Michie and Beryl Hartland were also represented, along with jazz trumpeter and artist Peter Allingham Henville (1925-2000). Several artists, particularly Reg Mount and Eileen Evans, had already established reputations during the war years, designing posters and leaflets. Mount’s work at AP included a poster for the 1955 film The Ladykillers, while Saul Bass designed the poster for Hitchcock’s Vertigo. In some ways Aubrey Rix became a victim of his own success, not least when his designs published in Letraset transfer sheets allowed his work to be used free of copyright. Tom Eckersley’s posters for Omo, Eno’s Salts and Guinness are advertising classics of their time.

Brian Sanders, who took over from Duffy as assistant to Adrian Flowers, had a studio at Dover Street, where he designed posters for films, including Oh! What a Lovely War, and also created photography sets for Adrian. Emulating the style of the Surrealist artist Rene Magritte, John Holmes designed the cover of Germaine Greer’s The Female Eunuch. Patrick Tilley, better-known now as a science fiction novelist and scriptwriter, was commissioned by BBDO to design covers for the Sunday Times magazines. Tilley also worked for Shell, and for the “Drinkapintamilkaday” campaign. Born in Essex in 1928, he had studied art at Durham. In 1955 he moved to London and established himself as a graphic artist. Several years later he began writing part-time, and in 1968 gave up design to work as a scriptwriter and novelist: his Fade-Out was published in 1974. In 1969, another AP artist, Peter le Vasseur, was commissioned by David Puttnam to create designs for The Sunday Times entitled ‘the History of Cinema’.
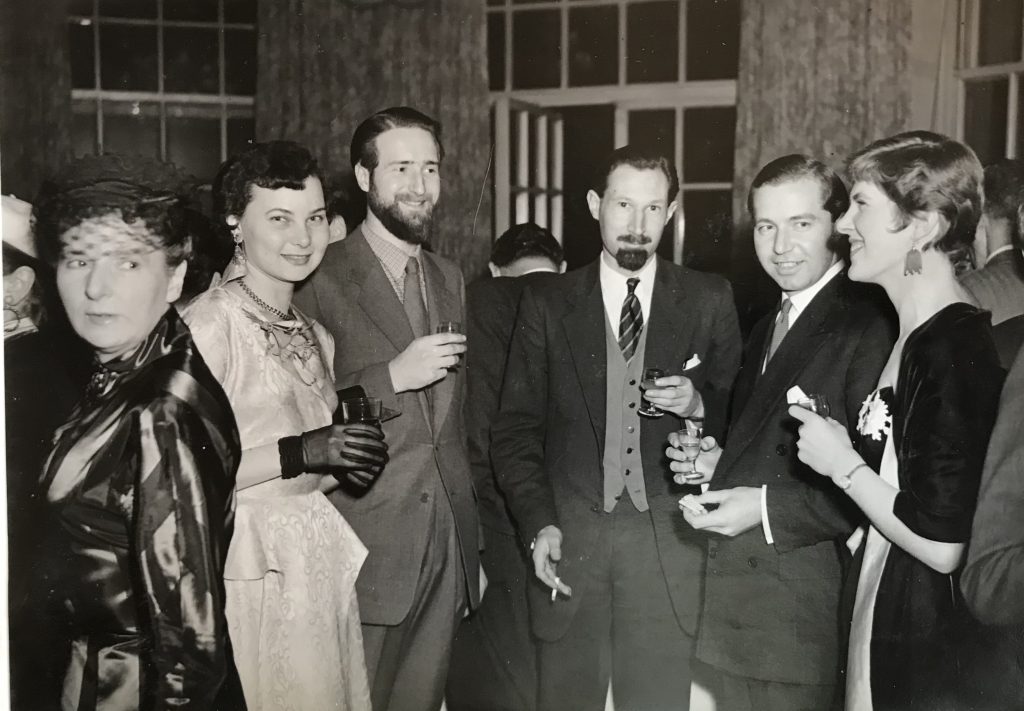

As Britain emerged from years of austerity and food rationing, much of the work of AP artists during the 1950’s was in advertising, and artists Susan Einzig, Harry Hants, Ken Wynn and Ben Ostrick worked on projects ranging from small drawings for the Radio Times to elaborate poster campaigns. In addition to posters and other design work, Sam Peffer, who had studied at Hornsey School of Art, designed covers for Pan paperback novels. The 1951 Festival of Britain provided a showcase for the talents of many AP members. However the golden age of art illustration was fading, and when editors found they could commission a photograph for twenty-five pounds, they baulked at spending three times that amount on commissioning original artwork. By the early 1970’s, the world of art illustration had all but collapsed.
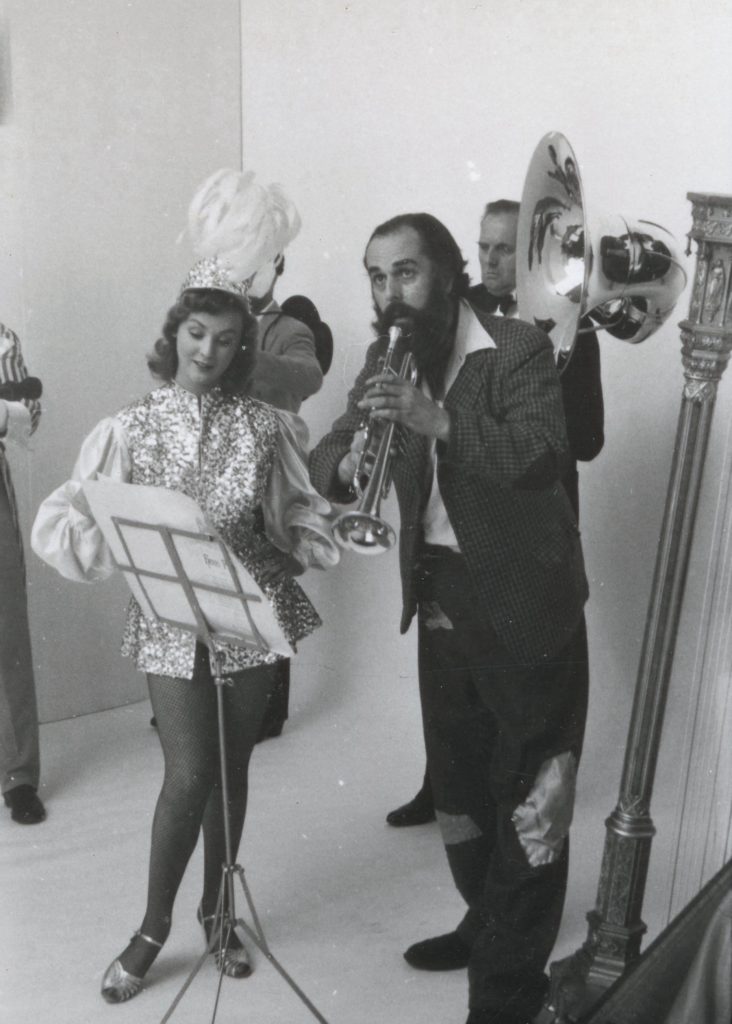

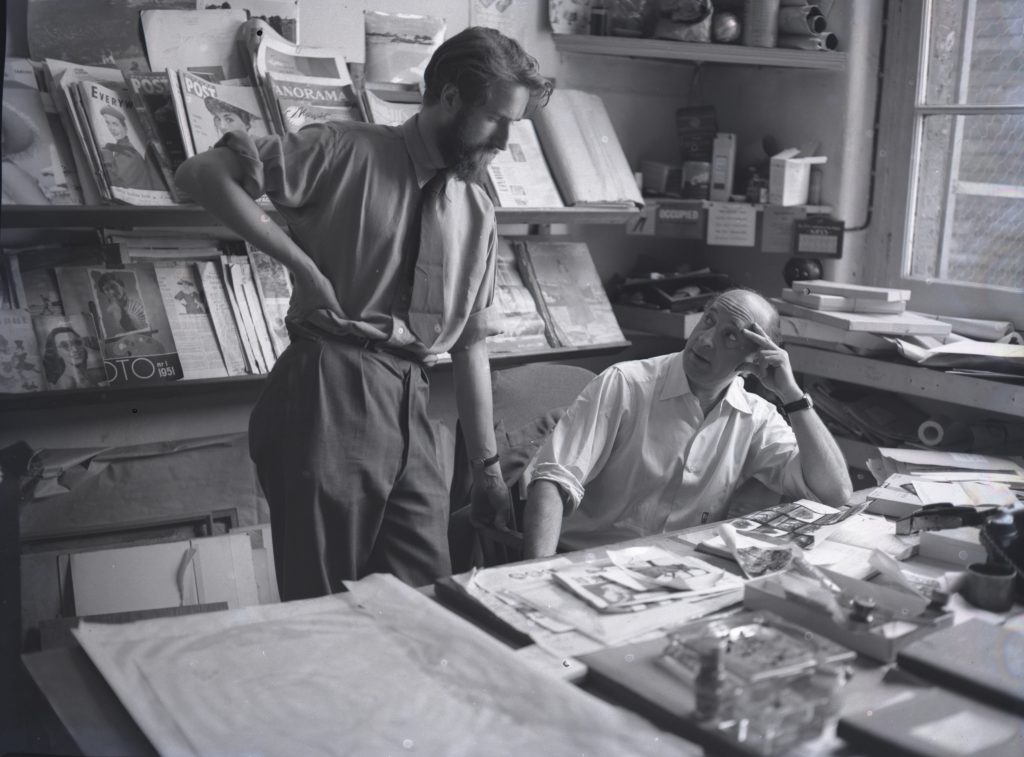
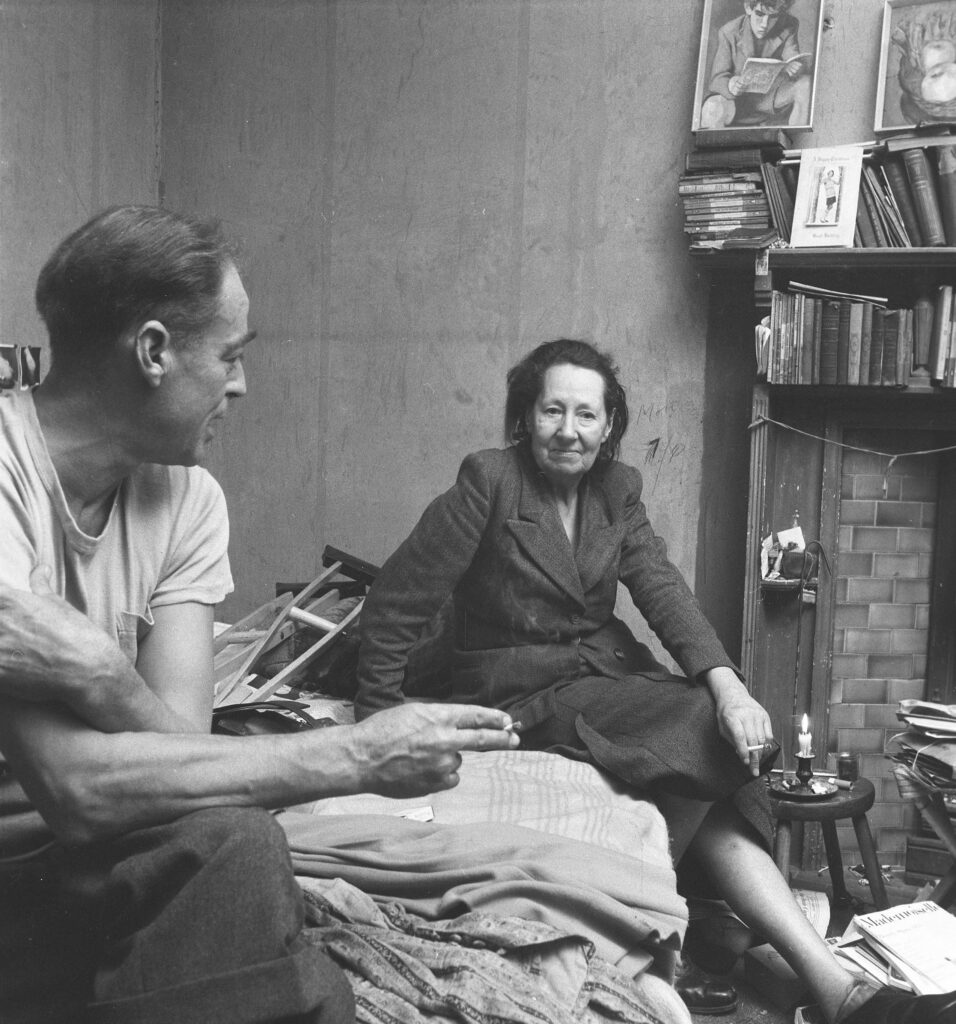
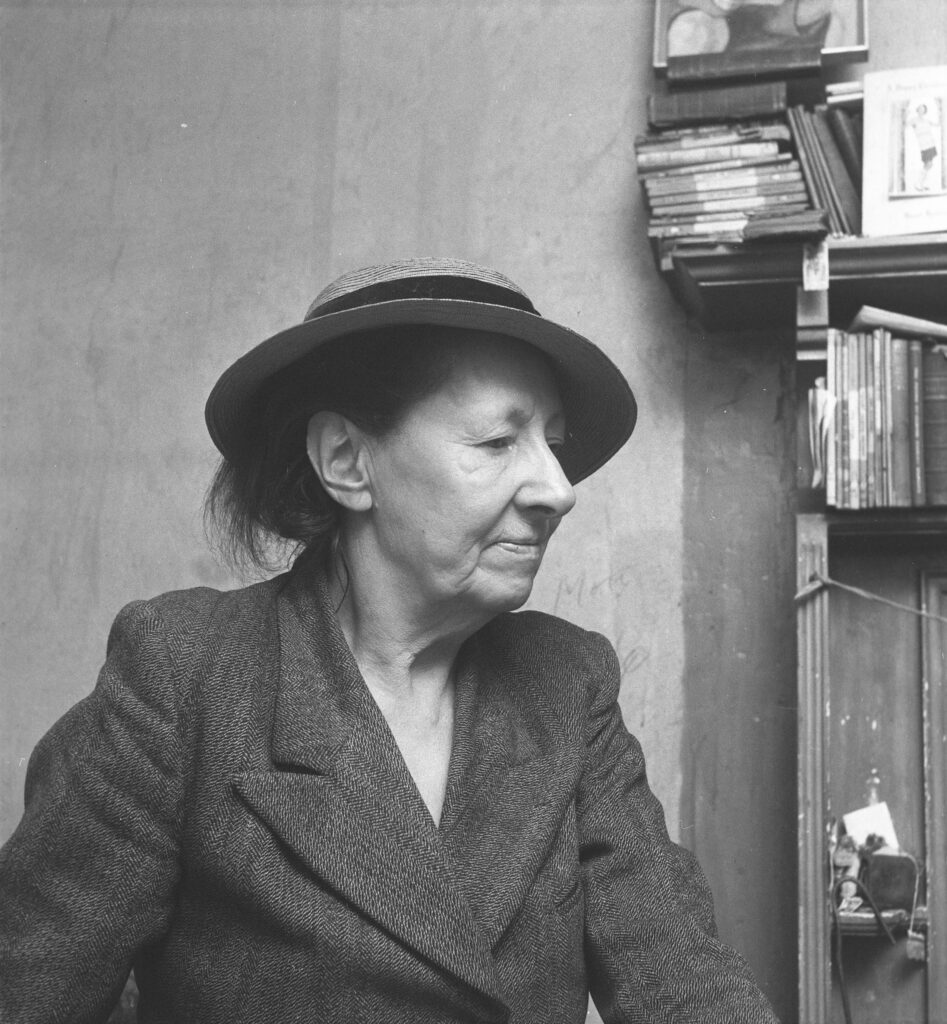
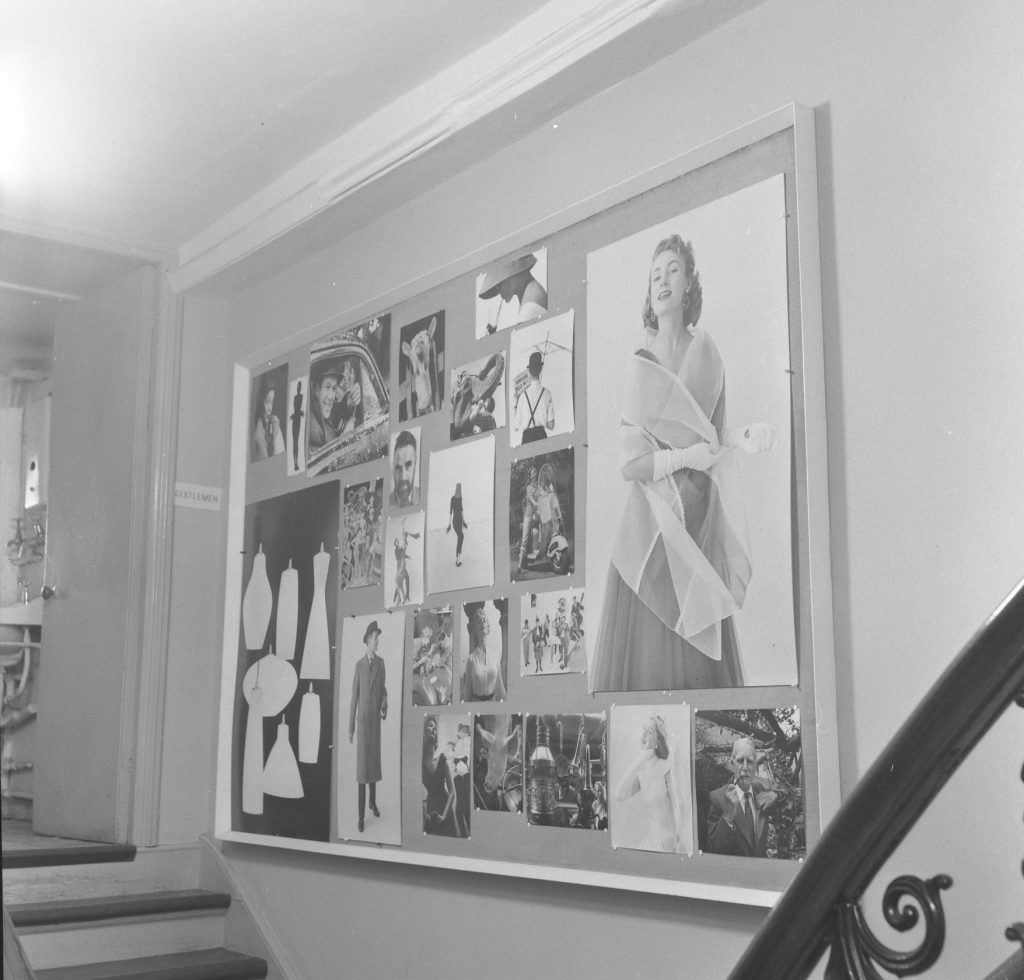
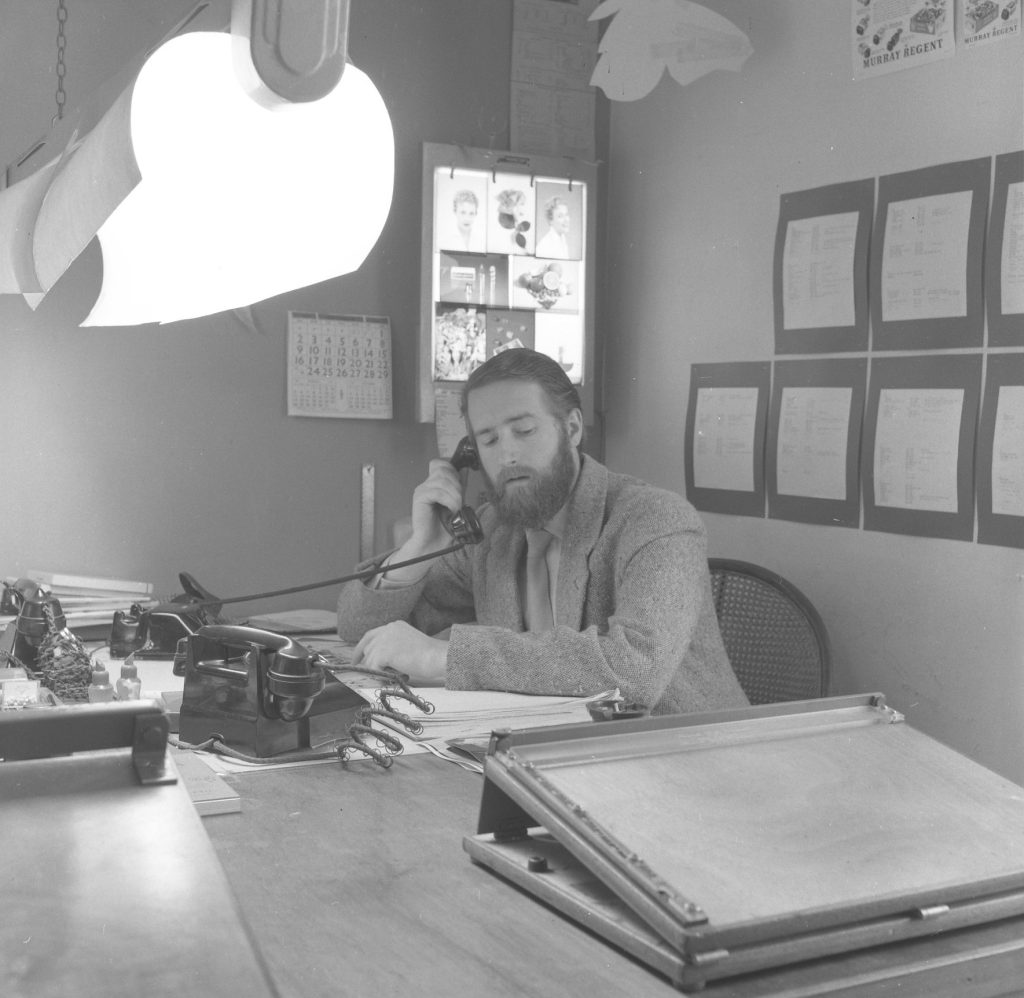
Nevertheless AP moved with the times, and in the early 1960s the company expanded, taking on the cartoonist Jak, the figurative artist Michael Leonard, and designers including Saul Bass, George Him, Herbert Leupin, Savignac, Feliks Topolski and Ruth Freeman. Photography, rapidly growing in importance in the world of advertising, also became a mainstay. In the Adrian Flowers Archive there are many portraits of AP members, taken around 1956. In October of that year, Adrian also took a series of photographs of the offices at Dover Street. His photographs give an insight into the day-to-day work at the company. In one image, pinned to a large noticeboard, can be seen a selection of portrait shots, photos of children and pets. A sequence of photographs shows a musical troupe preparing for a photo shoot. A tall step ladder had been set up, to enable photographs to be taken from above. The performers included a harpist, minstrel and a trumpet player, with trousers patched. Introducing the performers was a circus girl wearing sequined jacket and plumed headdress. In the background, a tuba player and guitarist made up the troupe. Dressed in a mantilla, a flamenco dancer stood at a window, looking down at the performers below, the whole ensemble a homage to Picasso’s ‘saltimbanques’. Adrian’s photos give an insight into behind the scenes; his lighting set-up included tall tripod luminaires with mirrored reflectors.
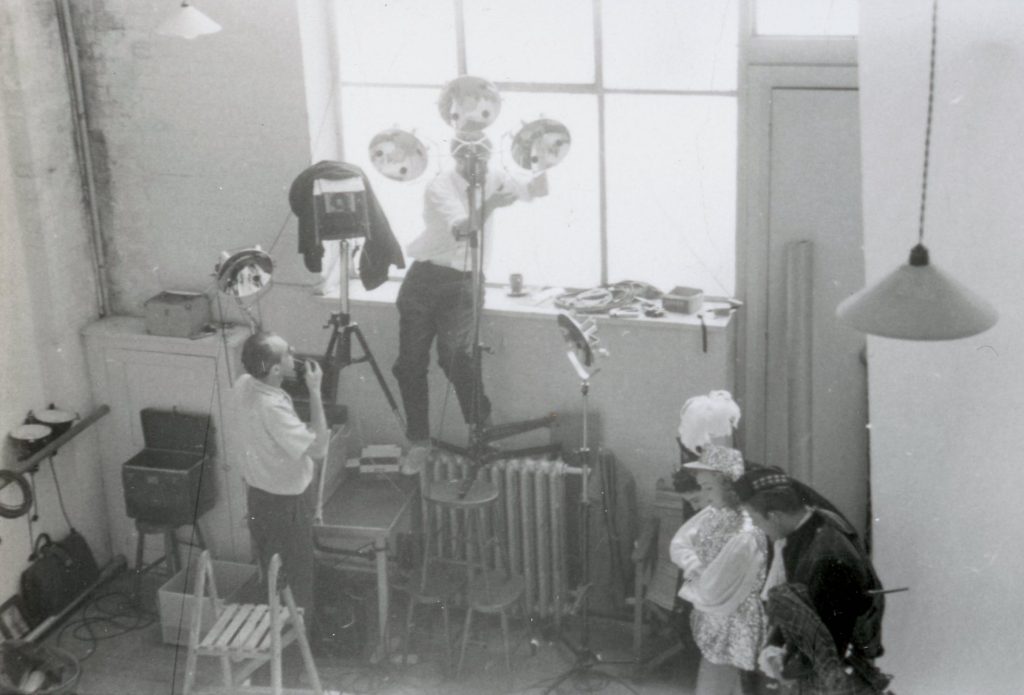

In one of Adrian’s photographs of the AP offices in Dover Street can be seen a framed page from Advertisers Weekly, entitled “Photography in Advertising”. Voted photograph of the month and winner of the Layton Award, Adrian’s photograph, featuring sugar tongs holding an ice cube above a glass, was subtitled ‘a picture that went better without a hand’. Taken for Monsanto Chemicals, it is linked to another of Adrian’s images, one that features a bouncing drip of water. He took on work sent his way by Zoltán Glass, including photographing the film star Robert Beatty, for Brylcreem. A photograph taken in 1956 shows Adrian, looking relaxed, reading a copy of the Manchester Guardian. On the front cover is a report on the Suez Crisis. [AF 2168] Adrian photographed diverse subjects, including a Victorian coach and horses in the street. Sandeman Port acquired a new logo, courtesy of Adrian’s photography. He also won a competition to advertise Australian canned fruit, and took pictures for the fashion pages of the Observer and Flair magazine. Although Adrian continued working with Artists Partners, in 1959 he moved to his own studio in Tite Street, Chelsea, where he was to remain for thirty years. During this period he continued exploring and experimenting, with the help of up to five assistants. There were in-house facilities at Tite Street for colour and black-and-white printing, while large sets were built in hired studios.

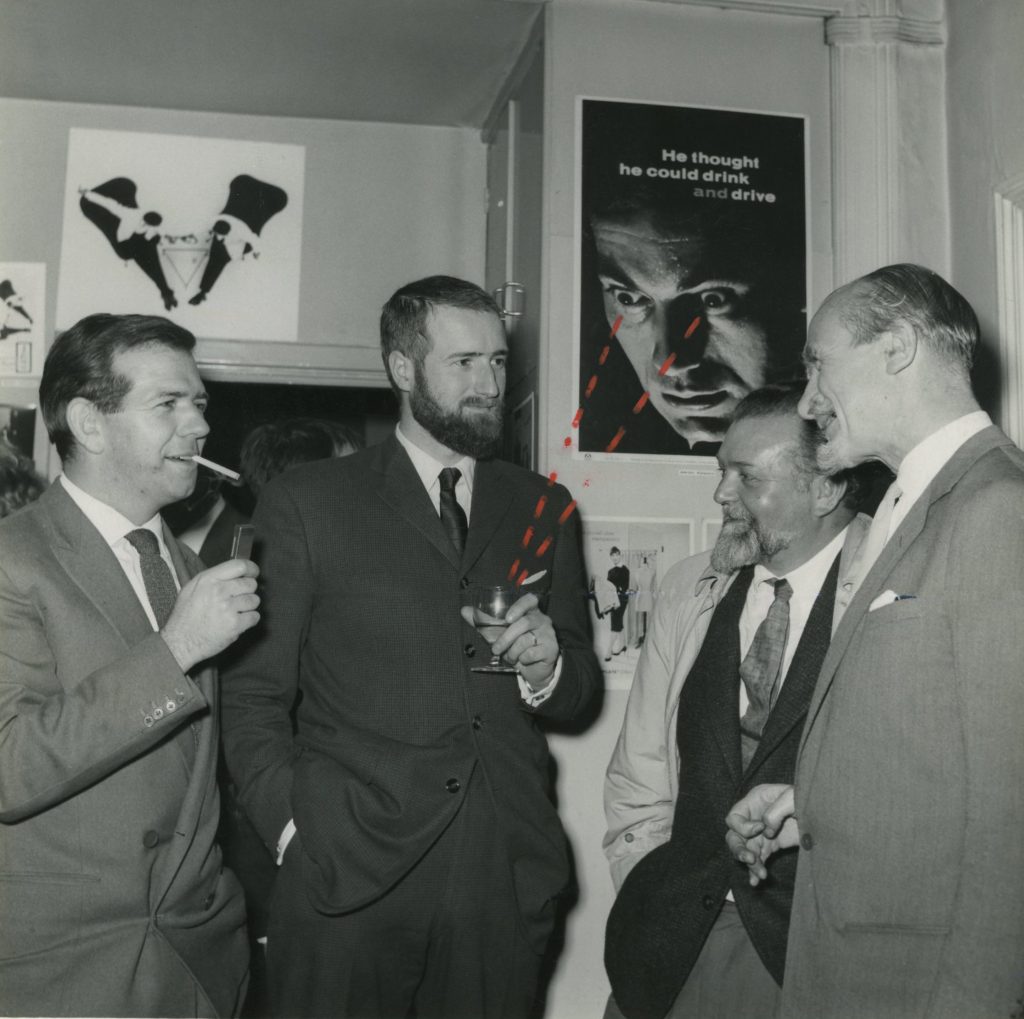
Artists Partners continued to flourish through the 1970’s and ‘80’s. Adrian’s old friend Len Deighton joined in 1969, as did the photographer Duffy, who had trained in Adrian’s studio. One of the most talented artists to join was Brian Sanders, whose illustrations have come to define the visual language of the 1960’s. Having started his career as assistant to Adrian, in the 1970’s Sanders was commissioned by Stanley Kubrick to make a visual record of the filming of 2001 A Space Odyssey. And some four decades later was commissioned to create a new body of work for the television series Mad Men. When Colmer Artists Agency ceased trading, several of their artists, including Virgil Pomfret, moved to AP. Some members, such as Barry Driscoll and Tom Adams, continued to work from their own studios. Christine Isteed took over front desk responsibilities at AP, while Don Candler’s sons Christopher and Tommy took turns managing the company, before Dom Rodi took over. Today, Artists Partners has Christine Isteed at the helm, serving as chairman and managing director.

Text: Peter Murray
Editor: Francesca Flowers
All images subject to copyright.
Adrian Flowers Archive ©






